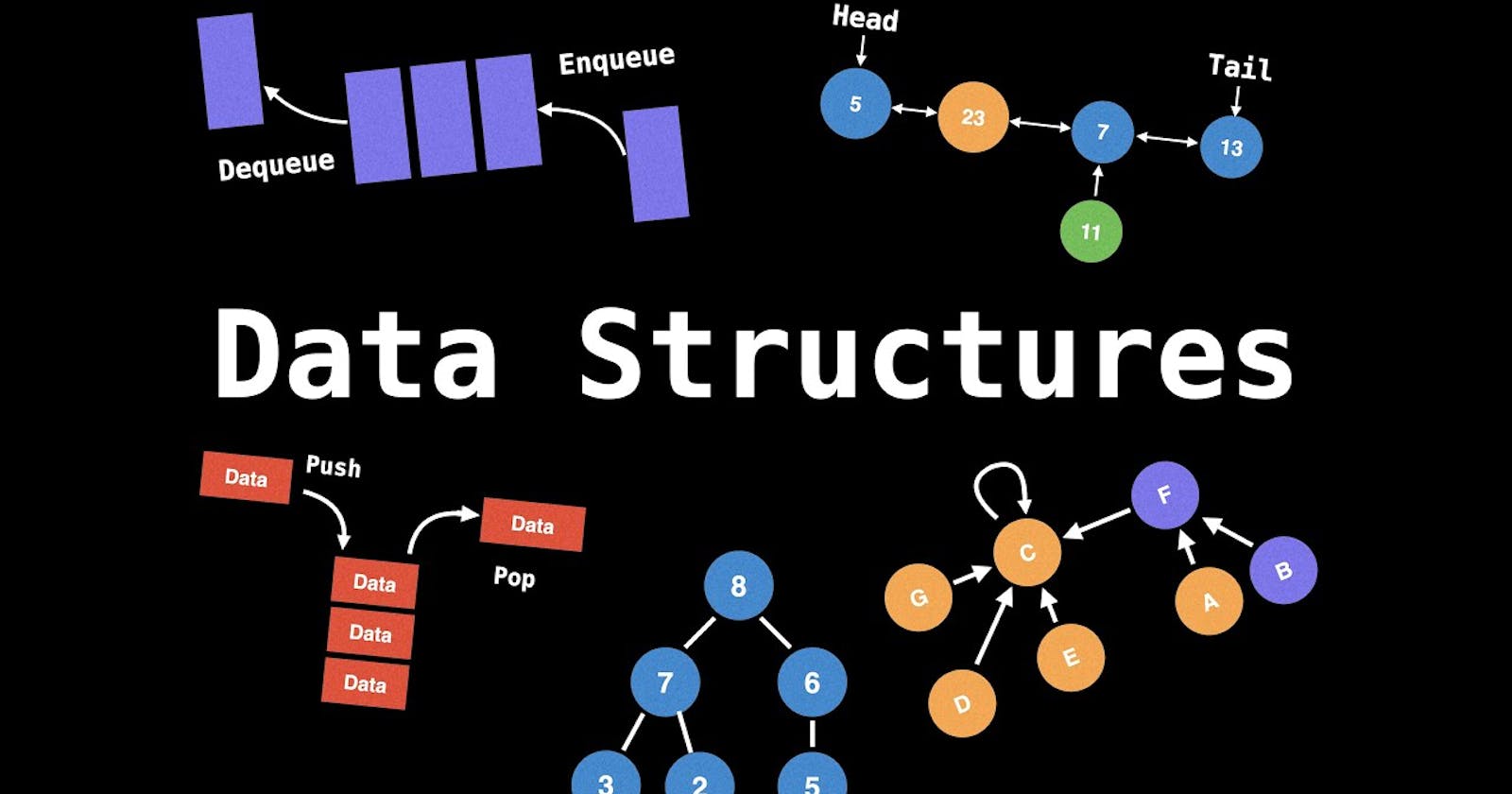
Data Structures:
- Data may be organized in many different ways, the logical or mathematical model of a particular organization of data is called Data Structure.
What is Data?
Data is singular or plural?

Data: Data are the raw facts/figures/descriptions regarding a thing or an entity.
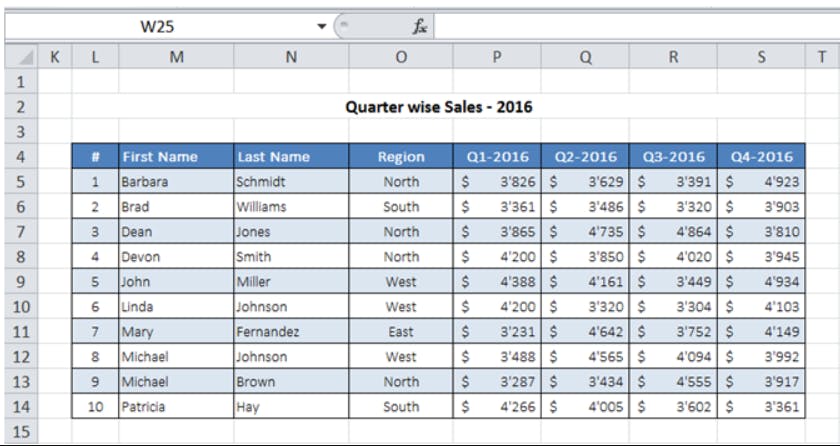
Example: There are so many employees in a company having a common name, so how you are going to differentiate them? By considering their other attributes or properties. Properties like: IDs, Job Roles, Age, Sex, Social Security Number, etc.
e.g.: ID Name Role
1 Robin Lee Data Analyst
What is Information?

A meaningful collection of data values processed in a particular order (processed data).
Like the example, we just saw in Data. Each of them is known as a data value.
So collecting data values and processing them in order or particular order.

Structure:
An infrastructure to hold data values systematically in a particular arrangement. This is also the collection of information or data values you can say right... it can also be referred to as frame/template/model.
Data Structures = Organised Data + Allowed Operations
Operations in Data Structures
8 operations are allowed for most of the Data Structures:
Creation
Traversal
Insertion
Deletion
Searching
Sorting
Concat
Merging
Creation:
Create a new Data Structure
Traversal:
Visiting each stored item exactly once.
Insertion:
Insert a new element to the data structure (at a given position).
Deletion:
Removing an item from the data structure.
Searching:
Finding the location of an item in the data structure.
Sorting:
Arranging the elements of the data structure in ascending, descending or alphabetical order.
Concat:
To join two or more data structures into a single unit.
Merging:
To join two or more data structures into a single unit followed by sorting.
That's it for this.
Introduction to Data Structures Part II coming sooon...